The Upcoming Ethereum Dencun Upgrade What Opportunities Will It Create?
Dencun is a compound word of Cancun and Deneb. Cancun is the name of the Ethereum implementation layer upgrade, while Deneb is the name of the protocol layer upgrade. Further, improve the staking infrastructure and reduce gas fees. There has yet to be an exact date for the upgrade, but it is expected to launch towards the end of 2023. The event is reported to mark a new milestone in the evolution of the Ethereum blockchain. The team has begun working on this much-anticipated update. So, what can we expect regarding changes to the network after Cancun-Deneb goes live? What opportunities are worth noting?

What is a Dencun upgrade?
Ethereum developers have confirmed an upcoming overhaul of the network, dubbed Dencun. Dencun is a compound word of Cancun and Deneb. Cancun is the name of the Ethereum implementation layer upgrade, while Deneb is the name of the protocol layer upgrade. Therefore, the Cancun and Deneb are collectively known as the Dencun upgrades.
The Ethereum Cancun-Deneb (Dencun) upgrade is an eagerly anticipated hard fork representing an essential milestone in the ongoing evolution of the Ethereum network. Building on the successes of previous upgrades, such as the recent Shanghai upgrade, Dencun aims to introduce significant improvements in scalability, security, and usability. In this section, we’ll dive into the details of this upgrade, exploring key features and enhancements that Ethereum enthusiasts and stakeholders can look forward to.
This upgrade includes five EIPs and is designed to add more data storage capacity and reduce fees. The promotion focuses on EIP-4844 and four proposed improvements, including EIP-1153, EIP-4788, EIP-5656, and EIP-6780.
Cancun: Improved scalability
The Cancun upgrade focuses on the execution layer of the Ethereum network. It introduces several Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) to enhance scalability and optimize gas efficiency. One notable EIP is EIP-1234, which regulates block rewards and delays the “difficulty bomb,” ensuring a smooth transition to Ethereum 2.0.
In the Ethereum Dencun, one of the critical advancements is the introduction of dank sharding and proto-dank sharding, which aims to extend the Ethereum blockchain and improve its efficiency.
Deneb: Improve Consensus and Security
The Deneb upgrade targets Ethereum’s consensus layer, primarily enhancing the security and consensus mechanism. One major EIP is EIP-2322, which introduces an upgrade to the Ethereum Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm, making it more powerful and efficient.
Completed EIPs for deployment
The Ethereum Dencun upgrade incorporates a number of EIPs that have already been finalized for deployment. Including:
- EIP-1559: This proposal introduces a new fee structure to improve user experience and reduce transaction fees. It offers a base fee that automatically adjusts based on network demand, simplifying fee estimation and reducing congestion.
- EIP-2929: This EIP enhances the security of the Ethereum network by increasing the cost of certain operations, making potential attacks more expensive and less attractive to malicious actors.
- EIP-2537 proposes a new Ethereum-specific opcode, making elliptical curve signature verification contracts more efficient and enhancing privacy and scalability.
Proto-Danksharding: Enhanced Scalability
Danksharding is a new sharding design that focuses on data availability. It introduces a new transaction format called “blob carrying transactions”, which allows the sender of a transaction to “attach” a large chunk of data to a transaction (think of it like you sending an email and an attachment).
This way, Ethereum will provide more space for tx data (transaction data) on Rollup protocols. Ethereum itself does not attempt to interpret these blob data directly. The protocol will use a “rule set” called KZG commitment to verify these blobs of data.
Proto-danksharding (also known as EIP-4844) is a proposal to implement most of the logic of danksharding, serving as the “scaffolding” for later danksharding development. Proto-danksharding is scheduled for mainnet on Shanghai Upgrade, which will take place in 6 -12 months after The Merge.
EIP-4844 introduces a blob-carrying transaction format that Rollup protocols will use to store data in the future. Blobs carry a large amount of data (~125 KB). They will have their own pricing mechanism, but it will generally be much cheaper than using calldata as it is today.
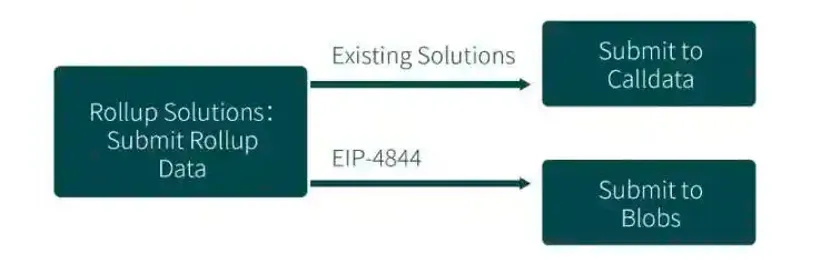
The fees for posting data to Ethereum make up many of the transaction fees that users pay on Rollup protocols. Proto-danksharding will significantly reduce this overhead for Rollup protocols by using the blob transaction format instead of calldata.
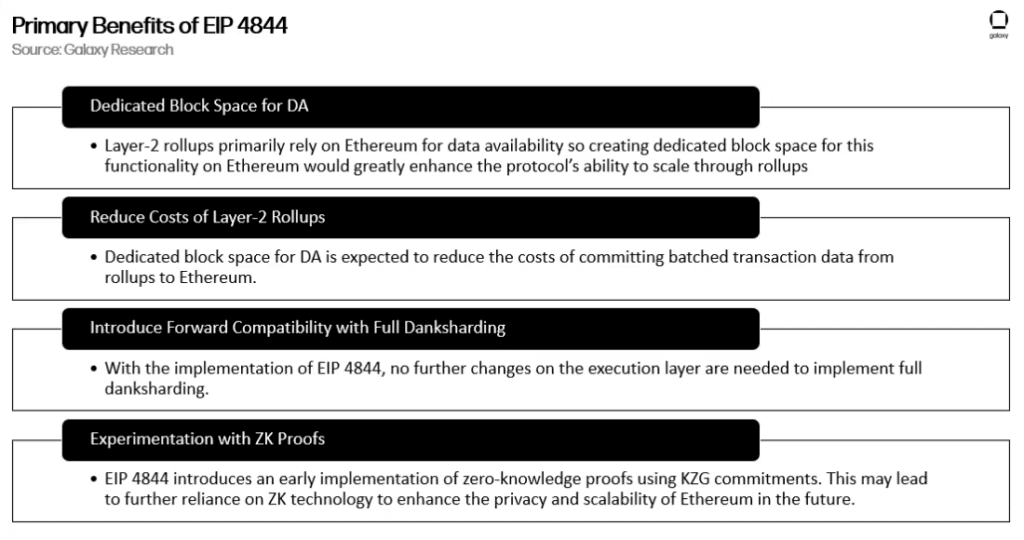
Through the introduction of danksharding and proto-danksharding, the Cancun-Deneb Ethereum Upgrade addresses one of the key challenges facing the Ethereum network: scalability. These innovations enable the network to handle higher volumes of transactions and smart contracts, facilitating the development and adoption of decentralized applications (dApps) built on the Ethereum platform.
As the Ethereum ecosystem grows, danksharding and proto-danksharding represent necessary steps toward achieving Ethereum’s long-term scalability goals. By optimizing network capacity and improving transaction efficiency, the upgrade sets the stage for a more sustainable and scalable Ethereum network.
Transactions shard blob: Improved transaction fees
EIP 4844 introduces a type of transaction known as a “block bearer transaction”. A blob is an abbreviation for “large binary object” representing a data payload of 125 Kilobytes. To create a transaction that carries the blob, aggregates send their data to the blobs and attach them to the blocks.
A blob-carrying transaction can contain up to two blobs. To incentivize the execution of these transactions, the upgrade will implement a multi-way EIP-1559 fee market. This feature will introduce a variable gas fee for blob-carry transactions based on supply and demand.
The main benefit of blob-carry transactions is cost efficiency.
EIP 4844 introduces a type of transaction known as “blob-carrying transactions”. A blob is an abbreviation for “binary large object” representing a data payload of 125 Kilobytes. To create a transaction that carries the blob, aggregates send their data to the blobs and attach them to the blocks.
A blob-carrying transaction can contain up to two blobs. To incentivize the execution of these transactions, the upgrade will implement a multi-way EIP-1559 fee market. This feature will introduce a variable gas fee for blob-carry transactions based on supply and demand.
The main benefit of blob-carry transactions is cost efficiency.
Rollup now permanently stores transaction data on Ethereum’s blockchain via Calldata. However, active Blob data is much cheaper than Calldata because it is not committed to the execution layer (Ethereum Virtual Machine). It also doesn’t last forever on the executor layer. Instead, Beacon nodes store them at the consensus layer, and after a month to a year, the blobs are removed. It is clear cached data from your laptop or device.
A polynomial commit scheme called KZG (named after its creators Kate, Zaverucha, and Goldberg) will verify transaction data posted in blobs. Like other zero-knowledge systems, KZG allows verification without revealing the entire contents of a blob.
Future ahead
While the previous Shanghai-Shapella upgrade allowed ETH to be withdrawn from staking, Cancun specifically aims to reduce transaction fees. In 2023–2024, the main focus will be on improving the scalability of the network.
The upcoming network upgrade planned for fall 2023 will take a similar approach to the protocol changes in April, with rollout scheduled for both the smart contract execution layer ( Cancun) and the PoS consensus layer (Deneb).
The main new feature of this upgrade is introducing a new transaction type called EIP-4844, also known as Proto-Danksharding, as described in the technical documentation. This is intended to further segment the network by temporarily storing and recovering previously deleted data. If successfully activated, transaction costs on the Optimism and Arbitrum networks are expected to be halved from current fees.
EIP-4844 is the first step on the road to scaling Ethereum, its importance and influence are no less profound than that of the Shanghai upgrade. Therefore, in the next upgrade of Ethereum Cancun, EIP-4844 will be promoted as the central task as soon as possible, and the estimated completion time is in the year’s second half.
It is expected that after the full implementation of IP-4844, the Total L2 transaction cost will decrease by a large extent, even to <0.001$, which will be a real boom for the users of total L2. For Ethereum, EIP-4844 is just the first step in a complete shard scaling solution, and implementing the first step will significantly reduce gas costs, giving the entire ecosystem more confidence that Ethereum will be more competitive and promising than other public chains.
DISCLAIMER: The information on this website is provided as general market commentary and does not constitute investment advice. We encourage you to do your own research before investing.
Join us to keep track of news: https://linktr.ee/coincu
Foxy
Coincu News



















