• Mar-a-Lago shooting prompts probe as timeline emerges
• Bitcoin holds as Saylor updates tracker, MSTR premium eyed
• Prediction markets face liquidity gaps amid insider risk
• Trump weighs limited Iran strike under War Powers Resolution
• Saylor Signals New BTC Buy as Bitcoin Slips Below $68K
• Bitcoin steadies as Atlanta Fed inflation gauge at 1.93%
• Bitcoin miners rethink cash as Bitdeer cuts BTC to zero
• Ethereum weighs AI agents for DAO votes after Buterin
• 4 Next Altcoins to Explode in the Next Bull Run: BlockDAG, Shiba Inu, MemeCore, and Pepe Bring Unique Potential!
• U.S. Tariff Authority narrows after Supreme Court ruling
At the core of blockchain ecosystems are Layer-1 protocols, the foundational layer that underpins all other blockchain layers. These protocols play a pivotal role as the sole entities responsible for maintaining the distributed ledger, validating transactions, and fortifying the network against potential threats. Today, Coincu will help you learn about this interesting topic.
What are Layer 1 protocols?
In the dynamic realm of blockchain technology, Layer 1 protocols stand as a foundational infrastructure platform that seamlessly connects Blockchain technology and Smart Contracts. This vital component serves as the backbone for the development of decentralized protocols and applications, paving the way for the evolution of the crypto market. Notable players in Layer 1 protocols include Ethereum, Solana, Near Protocol, and Cardano, each contributing to the diverse tapestry of decentralized innovations.
Within the crypto market, Layer 1 protocols are often referred to by various terms, such as Platform Blockchain, Smart Contract Platform, and Blockchain Layer 1, among others. Despite the diverse nomenclature, the most common, succinct, and widely adopted term is simply “Layer 1.”
Token issuance plays a pivotal role in the Layer 1 ecosystem, with platforms leveraging native tokens to foster development and engagement. Validators, key participants in the network authentication process, hold these tokens as a prerequisite for their involvement. Moreover, the original Layer 1 token doubles as a means to pay gas fees for transactions conducted on decentralized applications (dApps) built atop Layer 1.
The criteria defining blockchain Layer 1 protocols are stringent, encompassing general decentralization, robust security, and scalable infrastructure. To achieve enhanced scalability, Layer 1 protocols offer a range of customization options, employing diverse methods to ensure optimal performance and adaptability.
Knowledge of Layer 1 protocols
The significance of Layer 1 protocols in blockchain architecture
At the core of any blockchain architecture are its layers, each assigned a unique role in ensuring the system’s seamless operation. From data storage to network connectivity maintenance and consensus enforcement, these layers collectively shape the functionality of the blockchain. Four primary types of blockchains exist: public, private, consortium, and hybrid. The diversity in blockchain types leads to varied approaches to implementing their architecture, with no universal standard in place. The ultimate user-facing aspect, known as the application layer, provides specific products such as wallets, lending platforms, and staking services.
Despite being a critical component, users typically interact indirectly with smart contracts. Front-end interfaces of Web3 applications or APIs serve as the intermediary, providing a user-friendly gateway to the blockchain’s capabilities. In the realm of Layer 1 blockchains, Ethereum and Bitcoin stand out as the most dominant players in the Web3 landscape. Serving as foundational and self-sustaining chains, Layer 1 blockchains encompass all essential components of blockchain architecture. Public and permissionless in nature, they play a pivotal role in shaping the broader blockchain ecosystem.
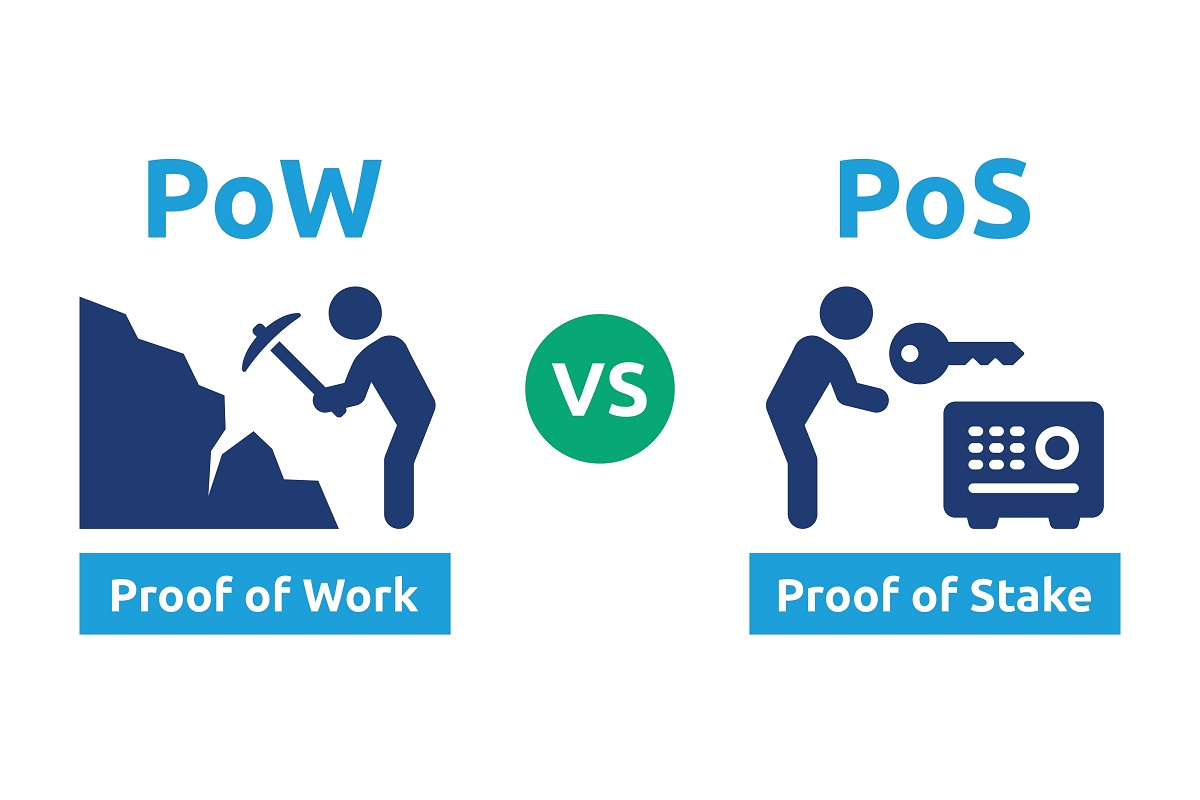
Consensus mechanisms of Layer 1 protocols
A consensus mechanism plays a pivotal role in validating entries into a distributed database, commonly known as a blockchain, and safeguarding its integrity. In the context of cryptocurrency, this becomes particularly crucial as it directly influences the security of the entire blockchain network.
Proof-of-Stake
In the dynamic world of cryptocurrencies, the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism is emerging as a revolutionary approach to processing transactions and ensuring the security of blockchain networks. This innovative method represents a departure from the traditional proof-of-work model, offering increased efficiency and sustainability.
One of the key advantages of the proof-of-stake mechanism lies in its ability to significantly reduce the computational work required to verify blocks and transactions. Unlike resource-intensive proof-of-work systems, which rely on hefty computing power, proof-of-stake introduces a more streamlined process. In this paradigm shift, coin owners contribute to the machines they possess, and instead of engaging in extensive computational work, they stake their coins as collateral. This collateral, or staking, serves as a commitment to participate in the validation of blocks, with the added incentive of earning rewards.
The selection of validators under the proof-of-stake system takes an interesting turn, moving away from the competitive rewards-based mechanism seen in proof-of-work. Validators are chosen randomly to confirm transactions and validate block information. This randomization not only enhances the security of the blockchain but also ensures a more inclusive and fair distribution of fees among coin owners.
Proof-of-Work
While proof-of-work has been a longstanding consensus mechanism for verifying cryptocurrency transactions through mining, it has faced increasing scrutiny due to its substantial energy consumption and potential centralization issues. In the realm of proof-of-work, the process of verifying cryptocurrency transactions hinges on mining, a computationally intensive task that demands a significant amount of energy. This energy-intensive nature has raised environmental concerns, as the continuous operation of network computers contributes to a blockchain system that is perceived as less environmentally friendly than its counterparts.
One of the primary drawbacks of proof-of-work is its susceptibility to centralization, a concern rooted in the competition between miners for rewards. The mining process involves solving complex mathematical problems, with successful miners reaping the rewards. However, this competitive environment has led to the emergence of a small number of mining pools wielding substantial influence, creating a de-facto centralization of the blockchain.
Sharding
Sharding is a promising method to enhance the scalability and efficiency of Layer 1 protocols. It represents a paradigm shift in blockchain management, introducing a system that breaks down the network into distinct database blocks known as “shards,” offering a glimpse into a more streamlined and accessible future for decentralized systems.
The core idea behind sharding lies in its ability to simplify blockchain management by distributing the network into separate, manageable shards. This departure from the traditional monolithic structure aims to optimize the processing of transactions and data, ultimately making blockchain operations more efficient and user-friendly.
How are Layer 1 protocols different?
At the core of Layer 1 blockchain technology lies the imperative trinity of decentralization, security, and scalability. Achieving this delicate balance necessitates the expertise of network architects and developers, who employ diverse strategies to enhance the system’s capacity to handle growth and ensure a robust foundation for the digital future.
Decentralization
Decentralization stands as the cornerstone of Layer 1 blockchain technology, embodying the ethos of distributed networks. Network architects and developers, equipped with their profound understanding of decentralized systems, play a pivotal role in designing and implementing structures that empower users and stakeholders. By dispersing control across the network, they fortify the resilience of the system against central points of failure, fostering a trustable and tamper-resistant environment.
Security
The bedrock of Layer 1 protocols lies in their commitment to robust security measures. Through intricate cryptographic mechanisms, these protocols employ advanced encryption techniques that not only secure transactions but also shield sensitive data from potential adversaries. The integration of distributed consensus further strengthens the security posture, creating a decentralized network of trust that is resilient against single points of failure.
Security requires the vigilant efforts of these experts. Through intricate cryptographic mechanisms, robust encryption, and advanced consensus algorithms, network architects and developers fortify the backbone of Layer 1 blockchain technology. Their expertise forms an impregnable defense against cyber threats, ensuring the integrity of data and transactions within the decentralized ecosystem.
Scalability
In the ever-expanding digital landscape, scalability emerges as a critical challenge. The ability of Layer 1 blockchain technology to handle growth without compromising performance is a testament to the ingenuity of network architects and developers. These professionals leverage various strategies, such as sharding and optimized consensus algorithms, to enhance the system’s capacity, accommodating the increasing demands of a dynamic and evolving user base.
Advantages and disadvantages of Layer 1 protocols
Advantages
The inherent security and decentralized nature make them robust foundations for various applications. Moreover, the integration of Smart Contracts within Layer 1 protocols introduces a groundbreaking shift, particularly in the realm of decentralized finance (DeFi). Activities deeply tied to finance, once reliant on third parties, now automatically execute through Smart Contracts, eliminating the need for trust in intermediaries.
Furthermore, Layer 1 protocols boast high customizability, adapting to the unique visions and missions of development teams. This flexibility allows for innovation and specialization within the blockchain space.
Disadvantages
Despite their advantages, Layer 1 protocols face certain drawbacks. Ethereum, a prominent Layer 1 blockchain, grapples with scalability issues, characterized by slow transaction speeds and high transaction fees. These challenges hinder Ethereum’s mass adoption potential.
Technical hurdles pose another obstacle, especially concerning the implementation of Sharding. Successful Sharding demands effective communication among different shards through the Beacon Chain, presenting a technical challenge for many developers, including the Ethereum team.
Moreover, Layer 1 protocols face compatibility issues with proof-of-work protocols. The security mechanism of Sharding relies on the proof-of-stake mechanism, a task that proves challenging in PoW protocols.
Proposed Solutions
- Layer 2 Protocols: These aim to shift implementation off-chain, reducing congestion on the main chain. However, achieving decentralization within Layer 2 networks poses a time-consuming challenge.
- High-Performance Layer 1 Protocols: Protocols like Solana and Internet Computer offer high-performance solutions to scalability issues. However, concerns about low decentralization persist, raising questions about the long-term sustainability of these networks.
- Layer 0 Protocols: Initiatives such as Polkadot, Cosmos, and Avalanche have entered the scene, attempting to address scalability concerns. Yet, they grapple with complexities and insufficient interactions between protocols, affecting the overall user experience.
The future of Layer 1 protocols
The ongoing Layer 1 protocol war has become a familiar narrative for seasoned investors. The continuous creation and innovation of Layer 1 protocols present a challenge for investors to stay abreast of market trends, as investing in a protocol that no longer aligns with the development trajectory can be a real risk.
Reflecting on the past, it becomes evident that the market is poised for another Layer 1 war in the future. Noteworthy contenders in this anticipated battle include Sui Blockchain, Aptos, Aleo, and Celestia among others. As the crypto market gears up for its next growth cycle, the probability of witnessing high-stakes competition between these prominent names is notably significant.
Investors are acutely aware that the success of Layer 1 protocols often hinges on their ability to stay ahead in terms of technology and innovation. The competition is not merely about establishing a blockchain but about introducing novel features and functionalities that cater to the evolving needs of the decentralized ecosystem.
Beyond scalability, cross-chain compatibility and interoperability have emerged as focal points for innovation. The ability of Layer 1 protocols to seamlessly communicate and share data with other blockchains is becoming increasingly essential. Projects like Polkadot and Cosmos are at the forefront of addressing this challenge, working towards creating a connected and interoperable blockchain ecosystem. The realization of cross-chain compatibility not only enhances the overall functionality of blockchain networks but also positions these protocols to cater to the diverse and evolving needs of users and dApps.
Top Layer-1 protocols according to criteria
Top Layer-1 protocols by market cap
Ethereum
The dominance of Bitcoin is a well-established fact. Likewise, Ethereum has asserted its supremacy in the Layer 1 protocols, and for it to continue this reign in the long term, the platform recognizes the imperative need for constant adaptation to the changing times. Ethereum currently has the second-largest market capitalization after Bitcoin.
Several upcoming updates highlight Ethereum’s commitment to maintaining its position at the forefront of innovation:
- The Surge: This update will replace the old development roadmap Sharding to EIP-4488 with the focused technology Danksharding. Integrate zkEVM from ZkSync, Scroll, Polygon,… and Rollup scaling solution with the goal of reaching 100,00 TPS in the future.
- The Verge: Supports validators to quickly and easily validate SNARK transaction proofs of zkRollup scaling solutions.
- The Scourge: Thoroughly handling issues related to MEV helps improve the user experience on the network.
- The Splurge: Completes a number of other upgrades to make the Ethereum network smoother.

BNB chain
BNB chain is a blockchain developed and combined from Binance Smart Chain and Binance Chain, with many changes in technology and development vision. It is in the top Layer 1 protocols, with a capitalization second only to Ethereum. BNB Chain will be a multichain platform, developing other sidechains besides BSC, thereby helping to increase blockchain performance, meet user needs, and develop protocols on this blockchain.
The BNB Chain is undergoing a transformative evolution, ushering in a breath of fresh air for projects and users alike. These changes span various facets, promising enhanced infrastructure, a redefined vision, and a shift towards greater decentralization.
- Infrastructure Overhaul: BNB Chain is undergoing a substantial infrastructure upgrade. The optimization of the user experience underscores the platform’s commitment to providing a seamless and efficient environment for its growing user base.
- Visionary Shift: Embracing a new vision, the BNB Chain is steering towards the development of MetaFi—a fusion of Metadata and DeFi.
- Decentralization Dynamics: Acknowledging previous concerns about centralization—stemming from a limited number of validators (only 21)—the BNB Chain is set to undergo a significant transformation in terms of decentralization. The perception of BSC blockchain as relatively centralized had deterred some developers from engaging with the ecosystem. However, the near future holds a promise of change.

Solana
Positioned alongside Ethereum and Cardano, Solana is engineered to facilitate peer-to-peer transactions, smart contract deployment, decentralized application development, and NFT transactions. What sets Solana apart is its unique consensus mechanism, utilizing both Proof of Stake (PoS) and Proof of History, enabling the network to handle thousands of transactions per second while maintaining remarkably low transaction fees.
Addressing the shortcomings of existing blockchain platforms, Solana aims to eradicate issues such as sluggish processing speeds, scalability limitations, and high transaction costs. The platform distinguishes itself by completing all transactions within minutes and at minimal costs. Boasting an impressive capability to execute up to 65,000 transactions per second and an ultra-fast block creation time of just 400 milliseconds, Solana establishes a foundation for decentralized operations and enhanced security. Consequently, many in the industry are heralding Solana as the future of blockchain technology.
Notably, Solana has earned the moniker “Ethereum Killer” and currently holds the third position among the top Layer 1 protocols in terms of market capitalization.
Top Layer-1 protocols by technology
Aptos- Sui
Aptos and Sui have emerged as groundbreaking platforms, each equipped with unique improvements poised to redefine the industry. Addressing key challenges, Aptos tackles scaling issues through its innovative Block-STM Algorithm, featuring parallel execution. On the other hand, Sui adopts the Narwhall and Bullshark approach to overcome the Mempool dilemma by strategically separating data transfer and consensus processes.
While Aptos and Sui may seem inseparable in their transformative journey, their collaboration is not coincidental. Both platforms trace their roots back to Facebook, particularly the Diem project. Following the setbacks of Diem, the project construction team regrouped and diversified their efforts within the crypto market, ultimately giving rise to the development of Sui and Aptos.
A significant commonality lies in the substantial financial backing both projects received before their mainnet launches, raising hundreds of millions of dollars. This financial support underscores the industry’s recognition of the potential inherent in Aptos and Sui, further solidifying their positions as leading Layer 1 protocols in the crypto market.
Monad
Monad is a focal point of attention across the entire crypto market. Notably, the buzz surrounding this platform is not solely attributed to airdrops or retroactive events but is predominantly fueled by the imminent launch of its testnet version, signifying a pivotal moment in its development trajectory. While the limelight often falls on factors like technology and development teams, Monad stands out as a compelling addition to the watchlist of any discerning long-term investor.
Drawing parallels with established platforms like Sui Blockchain and Aptos, Monad acknowledges that the execution phase is a critical bottleneck for achieving scalability on any underlying blockchain. Aligning with the insights of Aptos, Monad recognizes the limitations of conventional blockchains that organize transactions in a sequential order, known as Sequential Execution. In a strategic move to overcome this challenge, Monad sets its sights on Parallel Execution, a groundbreaking approach aimed at enhancing scalability and performance.
Celestia
Celestia is the first comprehensive Modular Blockchain in the crypto market, so although it does not call for too much capital like Aptos or Sui, Celestia still receives strong attention from the crypto community.
By separating the execution and consensus processes as well as data storage into distinct layers, Celestia aims to overcome the limitations of monolithic blockchains. This modular design not only enhances the platform’s scalability but also contributes to improved performance and adaptability. The separation of these fundamental components introduces a level of flexibility that is poised to elevate Celestia’s standing in the competitive blockchain landscape.
Top Layer-1 protocols by fundraising
NEAR Protocol
Since its inception in October 2020, NEAR has positioned itself as a formidable competitor to Ethereum, offering developers a platform to build decentralized applications (dApps). The blockchain gained significant traction, securing substantial funding that underscored the growing interest in its potential. Notably, in April 2022, a funding round led by Tiger Global injected $350 million into NEAR, just three months after a prior round raised $150 million in January of the same year.
The funding rounds marked a period of notable success for NEAR, propelling its cryptocurrency valuation to peak at over $12.5 billion in April. The substantial backing and valuation surge reflected the confidence investors had in NEAR’s vision and technology, positioning it as a key player in the competitive blockchain landscape. NEAR is one of the most successful Layer 1 protocols in fundraising.
Avalanche
The Avalanche project is a Layer 1 blockchain solution developed by Ava Labs. This project enables the launch of DeFi applications, financial assets, transactions, and other services. Besides, Avalanche is also a highly scalable open-source platform using the Proof of Stake mechanism.
Aptos
Aptos is a Layer 1 blockchain with scalability up to 160,000 TPS, completely solving the problems of transaction speed and transaction fees that still exist on Ethereum. Aptos was built by the same Core Team that built Diem Stablecoin and Blockchain on Facebook.
Aptos Labs raised $150 million in a Series A funding round that was led by FTX Ventures, the venture capital arm of crypto exchange FTX, and Jump Crypto in 2022.
DISCLAIMER: The information on this website is provided as general market commentary and does not constitute investment advice. We encourage you to do your own research before investing.