Superchain: A Scalable Network of Layer 2 Blockchains with Seamless Interoperability
Superchain is a groundbreaking advancement in blockchain technology that aims to address scalability issues and improve communication between blockchain networks. Built on the OP Stack by Optimism, Superchain offers a unified network of Layer 2 blockchains, also known as OP Chains.
The ecosystem enhances Ethereum’s capabilities, offering smoother interactions, increased scalability, and reduced transaction costs. In this article, we will explore what Superchain is, how it works, its advantages and challenges, and highlight some prominent projects within this ecosystem.
| Key Takeaways: – Superchain is an interconnected system of OP Chains built using Optimism’s OP Stack. – The network leverages a shared infrastructure with standardized security to optimize transaction speeds and reduce costs. – While Superchain offers high scalability, it faces challenges related to cross-chain security risks, and reliance on Ethereum’s infrastructure. |

What is Superchain?
Superchain is a network of Layer 2 blockchains developed using the open-source OP Stack platform created by Optimism. The individual chains within this ecosystem, or OP Chains, share a common codebase that ensures security, governance, and value consistency across the network.
By using OP Stack, Superchain allows OP Chains to interact seamlessly with each other, creating a cohesive ecosystem that extends Ethereum’s capabilities. This helps to address the scaling and fragmentation issues faced by Ethereum, paving the way for a future where blockchains can operate harmoniously and efficiently.
Read more: Optimism Update: Building A Superchain Ecosystem With Layer 2 Solutions
Structure and Operation
Structure
Superchain is based on the OP Stack, which is a suite of tools designed to build and manage OP Chains. The architecture consists of several core components, each of which plays a crucial role in ensuring scalability, security, and interconnectivity between chains. These components include:
- Data Availability Layer: Ensures the safe storage and accessibility of transaction data.
- Sequencing Layer: Collects and orders transactions before execution.
- Derivation Layer: Converts transaction data into a suitable format for processing.
- Execution Layer: Executes transactions and updates the state of the chain.
- Settlement Layer: Verifies and finalizes transactions between OP Chains and Ethereum.
Additionally, Law of Chains serves as a governance framework to maintain decentralization and consistency across the Superchain ecosystem.
How Superchain Works
Superchain functions as an ecosystem of interconnected OP Chains, all built on the shared infrastructure provided by OP Stack. This structure allows the Layer 2 blockchains within Superchain to optimize scalability and transaction costs.
One of the key features of Superchain is the seamless cross-chain interaction between OP Chains. Thanks to the inter-chain messaging mechanism, chains can communicate and exchange data effortlessly, enabling decentralized applications (dApps) to operate across different chains without barriers. Additionally, sharing sequencers across chains improves transaction processing speed and reduces latency.
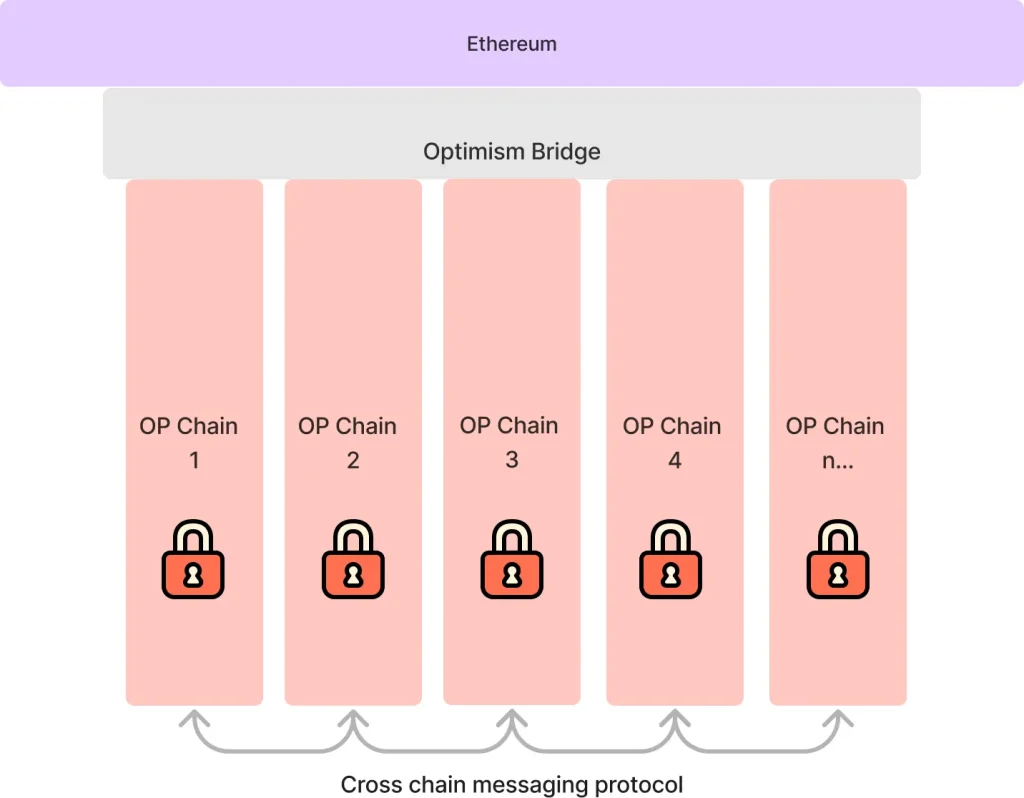
Security is also a major priority in Superchain’s operation. The ecosystem ensures security by applying uniform standards across all OP Chains while relying on Ethereum for final security. Shared authentication and governance mechanisms ensure compliance with overarching principles, preventing fragmentation and disconnection between chains.
| Did you know? The above operating mechanism enables Superchain to expand Ethereum’s capabilities and create a flexible, cost-effective environment for blockchain developers. |
Advantages of Superchain
Superchain brings numerous benefits to the blockchain ecosystem, driven by its scalability and high interconnectivity between OP Chains. Some of the key advantages include:
- High Scalability: Superchain processes transactions faster by using multiple OP Chains in parallel, reducing the load on Ethereum.
- Unified Security Model: All OP Chains in Superchain share a robust security system, minimizing risks and optimizing resources.
- Lower Deployment Costs: OP Chains can be created at lower costs by leveraging Ethereum’s consensus infrastructure.
- Seamless Interoperability: OP Chains can easily communicate with each other, creating a connected ecosystem conducive to dApp development.
- Synchronized Governance and Upgrades: The system is updated according to a unified roadmap, ensuring long-term stability and development.
Read more: OP Stack Brings Optimism Closer To Superchain Dream
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its many advantages, Superchain faces some challenges in terms of technology, governance, and security. Scaling the ecosystem and maintaining consistent performance across OP Chains require significant effort. Some of the key challenges include:
- Dependence on Optimism Technology: Since Optimism Superchain relies on OP Stack, any changes or updates to Optimism could impact the entire system.
- Scalability Issues: As the number of OP Chains increases, maintaining consistent performance and scalability becomes a complex task.
- Complex Governance: Synchronizing and controlling an ecosystem of numerous OP Chains requires an effective governance mechanism.
- Cross-chain Security Risks: As OP Chains communicate with each other, there is an increased risk of attacks and security breaches.
- Dependence on Ethereum: Superchain uses Ethereum as its security layer, meaning that any issues with Ethereum could affect the entire ecosystem.
Prominent Projects in the Superchain Ecosystem
Several significant projects are contributing to the growth and success of the Superchain ecosystem. Here are some notable examples:
Base
Base is a Layer 2 scaling solution built on Ethereum, developed by Coinbase in partnership with Optimism. Launched in August 2023, Base focuses on offering faster transactions and lower costs while maintaining Ethereum’s security. By supporting decentralized applications (dApps) in areas like DeFi, gaming, and social media, Base has become a significant player in the Superchain ecosystem.

OP Mainnet (Optimism Superchain)
Previously known as Optimism, OP Mainnet is a Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum built by OP Labs using the OP Stack. Launched in December 2021, OP Mainnet utilizes optimistic rollups to batch transactions and execute them offline, improving Ethereum’s scalability at lower costs. Managed by the Optimism Collective, OP Mainnet is one of the core pillars of the Superchain ecosystem.

Soneium
Soneium is another Layer 2 blockchain built on Ethereum, developed by Sony Block Solutions Labs in partnership with Startale Labs. Focused on bridging Web2 and Web3, Soneium supports applications in entertainment, gaming, and finance, offering a developer-friendly ecosystem that encourages innovation. Soneium is also part of the Superchain ecosystem, utilizing the OP Stack to build its Layer 2 chain.

Current Data from Superscan
Using Superscan, let’s take a closer look at the trends in recent months:
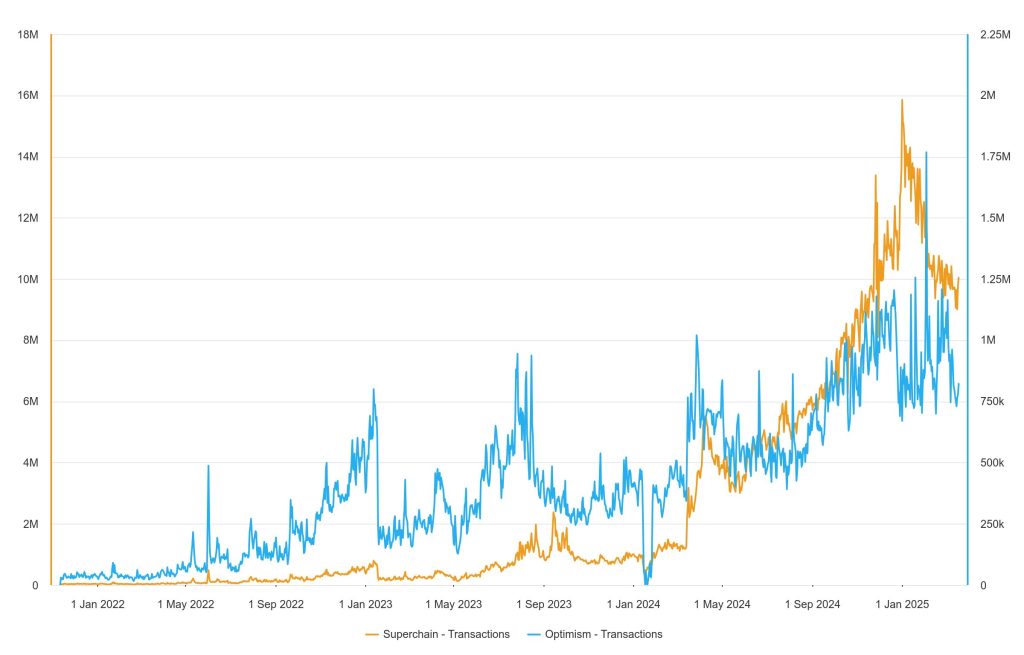
Superchain growth has been remarkable since the beginning of 2024 with over 10 million transactions per day in Q4. Almost from the beginning of the Layer 2 growth cycle, OP Mainnet, although following the same trend, could not match the transaction volume of OP Chains.
However, the transaction volume seems to have cooled down since the beginning of 2025 due to the market withdrawal process from Layer 2s.
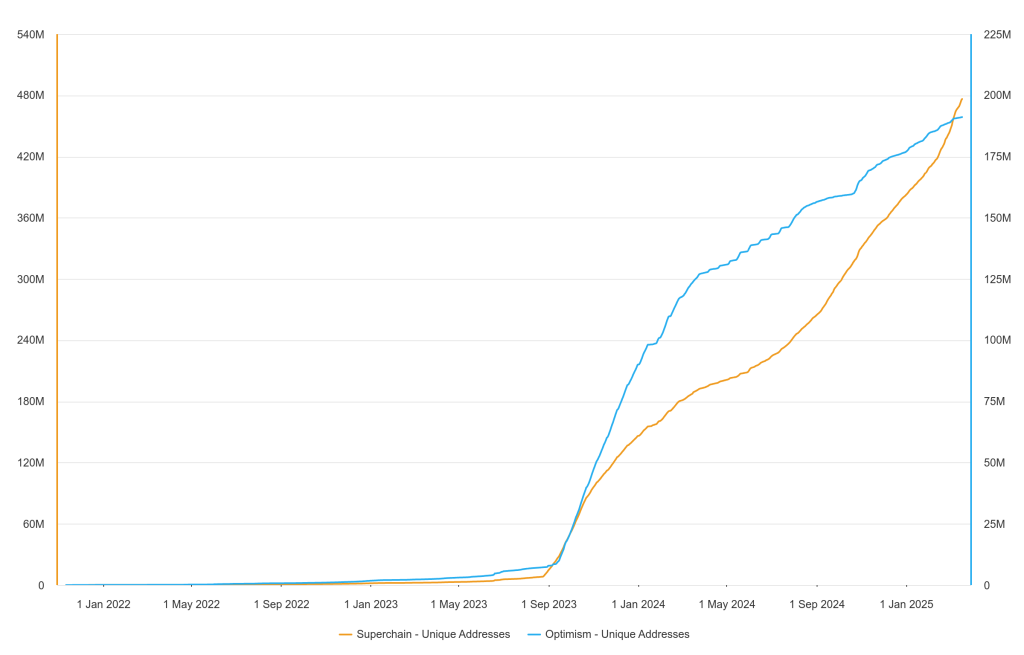
In terms of unique addresses, the figure of over 476 million to date has shown the strong growth of the network with increasingly steep hyperbolic growth. If compared to OP Mainet, 19 million unique addresses may be impressive but still far behind.
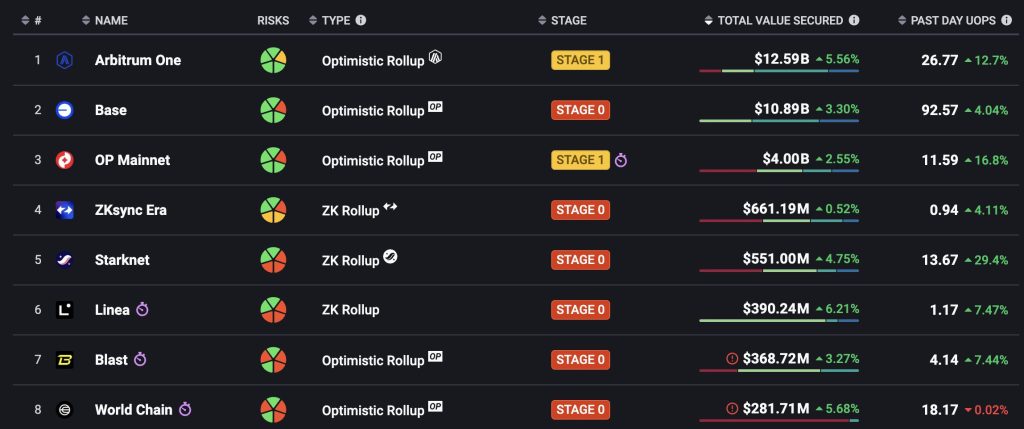
So how does it compare to the larger Layer 2 market? It all comes down to Base, which has now surpassed the $10 billion mark, making it the second-largest Ethereum Layer 2 protocol in the market today, behind only Arbitrum.
Impact of Superchain on the Blockchain Ecosystem
Superchain is making a significant impact on the blockchain ecosystem by enhancing scalability, fostering interoperability, and optimizing the user experience. By connecting multiple OP Chains through the OP Stack platform, Superchain offloads Ethereum, speeds up transaction processing, and reduces costs. This allows blockchain networks to process transactions in parallel, making the entire system more efficient.
Furthermore, Superchain promotes interoperability between blockchains by using the SuperchainERC20 standard, enabling cross-chain transactions without the need for wrapped tokens or bridges. This makes it easier for decentralized applications (dApps) to scale and for new blockchain projects to launch with low costs, facilitating innovation and growth in the ecosystem.
However, Superchain still faces challenges related to security, governance, and long-term scalability. Addressing these issues will be key to determining the future success of Superchain as a platform for decentralized, scalable blockchain networks.
Conclusion
Superchain represents a new era for blockchain technology, offering enhanced scalability, lower transaction costs, and greater interoperability between Layer 2 networks. With prominent projects such as Base, OP Mainnet, and Soneium driving the Superchain ecosystem, there are tremendous opportunities for developers and businesses to explore.
However, overcoming challenges related to security, governance, and scalability will be crucial for Superchain to reach its full potential. If these issues can be addressed, Superchain could become a vital platform for creating a decentralized, efficient, and sustainable blockchain ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions
| DISCLAIMER: The information on this website is provided as general market commentary and does not constitute investment advice. We encourage you to do your own research before investing. |











