| Key Points: – Ethereum’s burn rate has hit an all-time low, reflecting a sharp decline in on-chain activity. – The network burned just 53.07 ETH ($106,000) in a day, the lowest since EIP-1559’s launch. – Growing reliance on Layer-2 solutions like Arbitrum and Base is diverting transaction volume. – ETH’s inflation rate is now positive, raising concerns about its long-term deflationary model. |

Ethereum’s burn rate plummeted to its lowest level since the launch of EIP-1559, highlighting weak demand for blockspace. With Layer-2 networks attracting more activity, Ethereum’s long-term supply dynamics are shifting, prompting concerns among investors.
The decline in Ethereum’s burn rate signals a fundamental shift in the network’s economic model. EIP-1559 was designed to reduce ETH’s supply by burning a portion of transaction fees, but with fewer transactions on the mainnet, the deflationary mechanism is weakening. Analysts now question whether Ethereum can maintain its value proposition as a deflationary asset while transitioning to a multi-layered ecosystem.
Ethereum’s Burn Rate Drops to a Historic Low
Ethereum’s burn rate has hit its lowest point since the launch of EIP-1559, a major upgrade aimed at reducing inflation by burning a portion of transaction fees. On March 23, only 50.03 ETH ($104,812) was burned, marking the weakest burn day in Ethereum’s history.
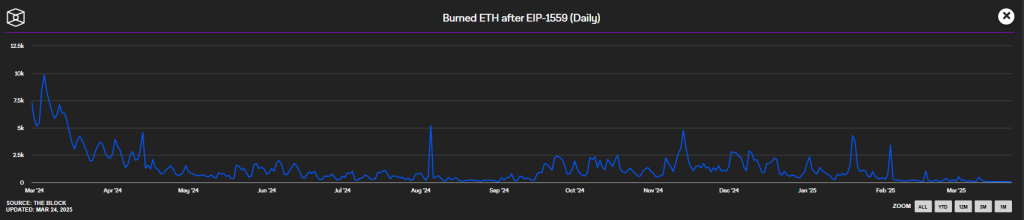
This sharp decline signals a drop in network demand, as the Ethereum burn mechanism is directly tied to transaction activity. When gas fees are high, more ETH is burned, sometimes even turning Ethereum into a deflationary asset.
However, recent data from Ultrasound.money projects Ethereum’s supply to increase by 0.76% annually, indicating a shift back to inflationary issuance.
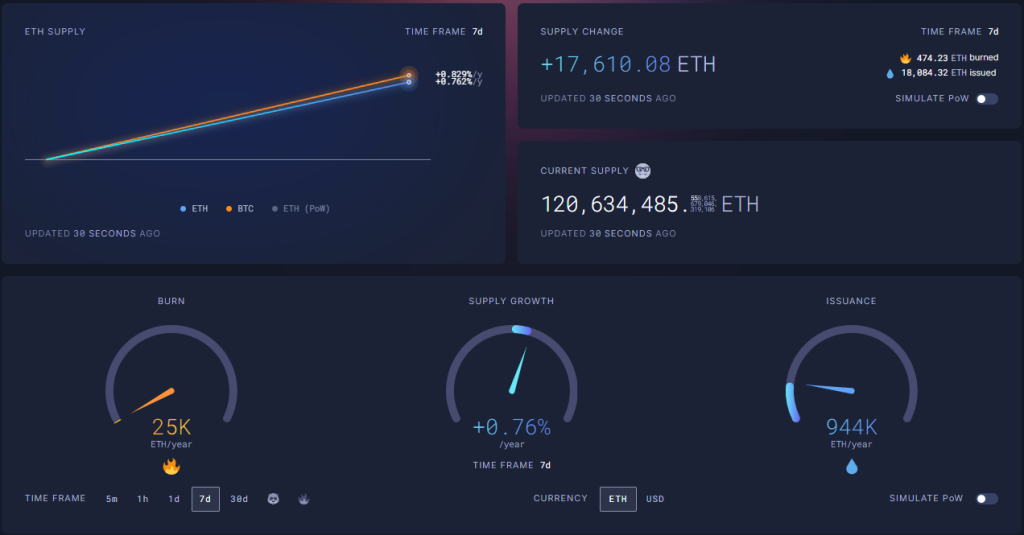
Ethereum Faces Competition from Layer-2 Networks
A major reason behind Ethereum’s declining burn rate is the rapid rise of Layer-2 scaling solutions like Arbitrum, Optimism, and Base. These networks offer cheaper and faster transactions, attracting users who would have otherwise interacted directly on Ethereum’s mainnet.
Layer-2 solutions still rely on Ethereum for security, but they divert transaction fees away from the base layer, reducing ETH burns. As a result, Ethereum’s core network sees fewer transactions, lower fees, and weaker deflationary pressure, making it less attractive as a long-term store of value.
ETH’s Price Outlook Weakens Amid Declining Usage
The combination of lower transaction volume reduced ETH burns, and Layer-2 competition has led analysts to rethink Ethereum’s future price potential. Standard Chartered recently slashed its ETH price target for 2025 from $10,000 to just $4,000, citing diminishing value capture on Ethereum’s mainnet.
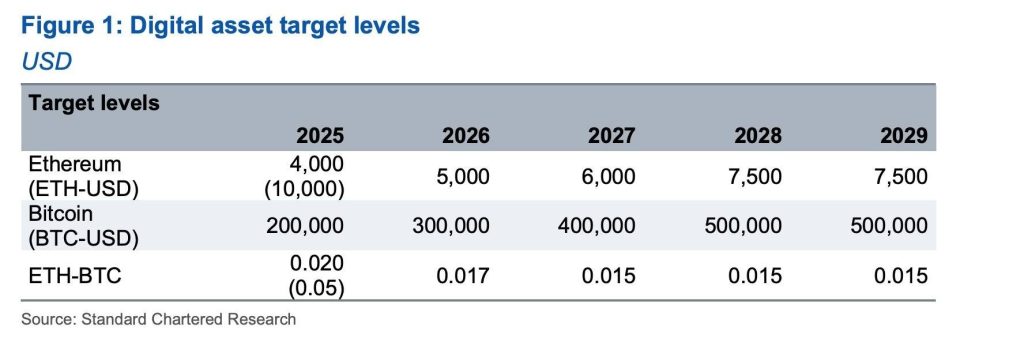
While Ethereum remains the dominant smart contract platform, its economic model faces new pressures. If Layer-2s continue absorbing transaction activity, Ethereum’s deflationary narrative may weaken, potentially limiting its long-term upside.
| DISCLAIMER: The information on this website is provided as general market commentary and does not constitute investment advice. We encourage you to do your own research before investing. |