The Beacon Chain is a critical component of Ethereum 2.0, which is an upgrade to the existing Ethereum blockchain. It serves as the storage and management system for validators and facilitates the coordination of shard chains. The Beacon Chain was launched on December 1, 2020, at noon UTC, marking an important milestone in the Ethereum ecosystem.
As a proof-of-stake blockchain, the Beacon Chain plays a crucial role in keeping the Ethereum 2.0 system operational. It can be thought of as a towering lighthouse amidst a vast sea of transaction data. Its main tasks include continuous scanning, validating, vote collection, and reward distribution to validators who accurately attest to blocks. It also penalizes validators who are offline or engage in malicious activities by reducing their ETH rewards.
The primary function of the Beacon Chain is to manage the proof-of-stake protocol itself and oversee all shard chains. Shard chains are individual chains that will enhance Ethereum’s data capacity, resulting in a faster and more scalable network. The Beacon Chain is responsible for managing validators and their stakes, nominating block proposers for each shard, organizing validator committees to vote on proposed blocks, enforcing consensus rules, applying rewards and penalties to validators, and serving as an anchor point for shards to register their states and facilitate cross-shard transactions. It is important to note that the Beacon Chain does not support smart contracts; this functionality is reserved for the shard chains.
Let’s delve deeper into the role of the Beacon Chain in the Ethereum 2.0 ecosystem. The Beacon Chain acts as the coordination mechanism for the new network. It is responsible for creating and validating new blocks and rewarding validators with ETH for maintaining network security.
Proof-of-stake addresses the limitations of proof-of-work blockchains, such as accessibility, centralization, and scalability. In a proof-of-stake system, the Beacon Chain randomly selects validators (each with a stake of 32 ETH) to propose new blocks. These blocks are then voted on by other validators, who attest to their validity. This consensus mechanism ensures that the blockchain remains secure and resistant to attacks.
Validators play a crucial role in the Ethereum 2.0 network. They are responsible for validating transactions, proposing blocks, and securing the network by staking their ETH. Validators are selected based on their reputation and the amount of ETH they are willing to stake as collateral. The higher the stake, the more chances a validator has of being selected to propose blocks. Validators are rewarded with ETH for their participation and are also subject to penalties if they misbehave, such as going offline or engaging in malicious activities.
By leveraging the power of proof-of-stake, the Beacon Chain enables Ethereum to become more energy-efficient, scalable, and secure. It eliminates the need for energy-intensive mining and allows a greater number of transactions to be processed simultaneously, thanks to the introduction of shard chains.
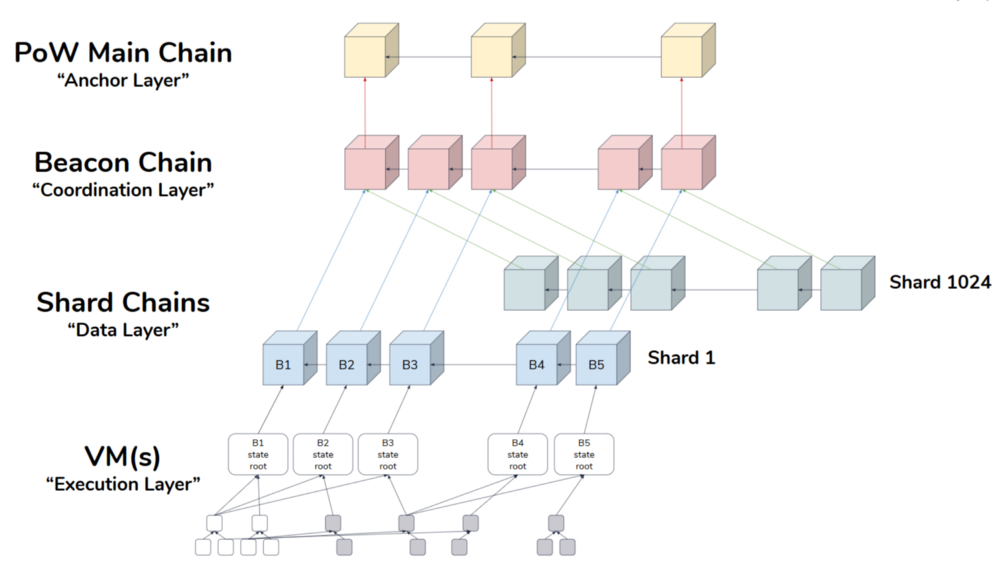
The Beacon Chain serves as the backbone of the Ethereum 2.0 network and governs and coordinates all 64 separate shard chains. Each shard chain operates independently, processing its own transactions and storing its own data. The Beacon Chain ensures the overall consensus of the network and allows for communication and coordination between different shards.
The introduction of shard chains is a significant upgrade for Ethereum, as it will increase the network’s capacity to handle a larger number of transactions. This scalability improvement is essential for Ethereum’s continued growth and adoption, especially as decentralized applications and DeFi projects gain momentum.
With the Beacon Chain and proof-of-stake system in place, Ethereum is transitioning from a single-chain network to a multi-chain network. This transition is occurring in multiple phases, with the Beacon Chain being the first step. The subsequent phases will involve the implementation of shard chains, which will further enhance Ethereum’s scalability and decentralization.
As a newbie in the blockchain space, understanding the Beacon Chain is crucial in grasping the fundamentals of Ethereum 2.0. The Beacon Chain acts as the central coordinating entity that manages validators, facilitates consensus, and governs shard chains. Its role in maintaining network security, scalability, and decentralized governance makes it a vital component in the evolution of the Ethereum ecosystem.
In conclusion, the Beacon Chain is an essential part of Ethereum 2.0 that serves as the storage and management system for validators and coordinates the operation of shard chains. It plays a critical role in maintaining network security, scalability, and decentralized governance. By transitioning to a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism and introducing shard chains, Ethereum aims to address the limitations of traditional blockchains and provide a more energy-efficient, scalable, and secure platform for decentralized applications and financial activities.














