Bitcoin Spot ETF Applications: A Comprehensive List of All Companies, Including Wall Street
This comprehensive exploration delves into the landscape of Bitcoin Spot ETF applications, analyzing the efforts of various companies, including those from the hallowed halls of Wall Street, to bring these investment vehicles to market.
The quest for approval from regulatory bodies, notably the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), adds layer of complexity to this unfolding narrative. Understanding the dynamics of Bitcoin Spot ETF applications is not merely an exercise in financial innovation but a crucial step towards integrating the cryptocurrency market with established financial markets.
What is a BTC Spot ETF?
- Underlying Asset: The ETF holds actual Bitcoin as its underlying asset. Investors in the ETF indirectly own a share of the Bitcoin held by the fund.
- Tracking the Spot Price: The ETF is designed to track the spot price of Bitcoin as closely as possible. This means that the value of the ETF should reflect the current market value of Bitcoin.
- Exchange-Traded: Like traditional ETFs, Bitcoin Spot ETFs are traded on stock exchanges. This provides investors with a more accessible and regulated way to gain exposure to the price movements of Bitcoin without directly owning or storing the cryptocurrency.
- Creation and Redemption: Authorized participants, typically large financial institutions, can create or redeem shares of the ETF by exchanging Bitcoin for shares or vice versa. This process helps keep the ETF’s market price in line with the net asset value (NAV) of its underlying assets.
- Regulation: Bitcoin Spot ETFs are subject to regulatory approval by financial authorities in the jurisdictions where they operate. In the United States, for example, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) plays a crucial role in approving or disapproving ETF applications.
Requirements For Bitcoin Spot ETF Applications
Bitcoin Spot ETF applications can vary based on the regulatory jurisdiction, particularly in the United States, where the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) plays a significant role. Generally, the process involves rigorous scrutiny to ensure investor protection and market integrity. Here are some key requirements and considerations that issuers typically need to address when submitting Bitcoin Spot ETF applications:
- Regulatory Approval:
In the United States, ETFs must register with the SEC. The application process involves submitting a registration statement, which includes detailed information about the ETF’s structure, investment objective, risks, and operations. - Custody and Security:
Issuers need to demonstrate secure custody arrangements for the Bitcoin held by the ETF. This is crucial to prevent theft, loss, or any compromise of the assets. - Market Manipulation Concerns:
The SEC is concerned about potential market manipulation in the underlying cryptocurrency markets. Applicants need to address how they plan to mitigate and detect market manipulation, ensuring fair and orderly markets. - Market Surveillance:
Effective surveillance mechanisms are required to monitor the underlying Bitcoin markets for any suspicious activities. This helps in maintaining market integrity. - Arbitrage Mechanisms:
ETFs typically rely on an arbitrage mechanism to ensure that the ETF’s market price closely tracks its net asset value (NAV). Issuers need to explain how this mechanism will work, facilitating the creation and redemption of shares. - Disclosure and Transparency:
Issuers must provide comprehensive and clear disclosure about the ETF’s investment objectives, strategies, risks, fees, and other relevant information. Transparency is a key element to empower investors to make informed decisions. - Market Liquidity:
The liquidity of the underlying Bitcoin market is a consideration. A liquid market is generally seen as more suitable for ETFs, as it helps in efficient price discovery and trading. - Legal and Compliance Framework:
Ensuring compliance with existing securities laws and regulations is paramount. Issuers need to work within the legal framework to address any potential legal concerns. - Ongoing Reporting and Compliance:
ETFs are required to provide ongoing reporting to regulatory authorities. Compliance with regulations and periodic reporting on the fund’s activities, holdings, and financial performance is crucial. - Experienced Intermediaries:
The involvement of experienced intermediaries, such as authorized participants and market makers, is often required to facilitate the creation and redemption of ETF shares and maintain market liquidity.
List of Companies Seeking Bitcoin Spot ETF Applications
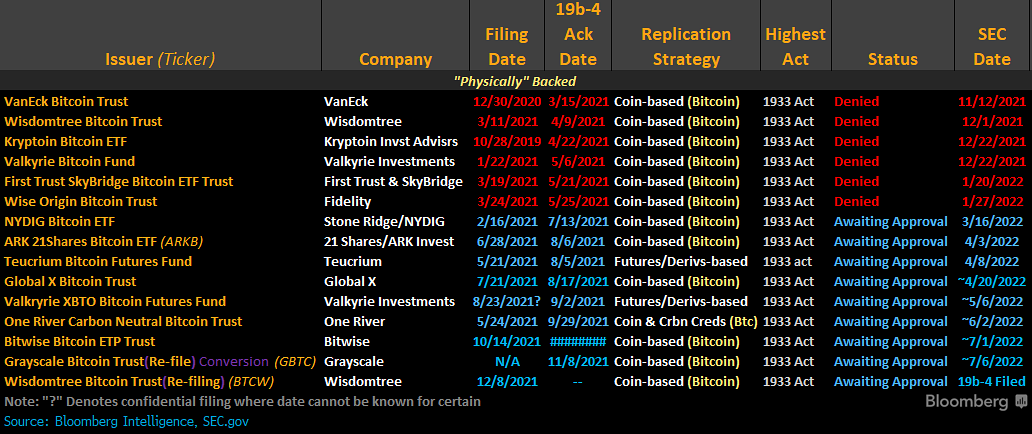
- BlackRock: Founded in 1988, BlackRock stands as the world’s largest asset management company, boasting assets exceeding $8.5 trillion. When BlackRock submitted its Bitcoin ETF application on June 15, 2023, Bitcoin experienced a notable surge of over $5,000 within a week.
- GrayScale: As a dominant player in the crypto asset management realm, GrayScale has been actively involved in crypto over-the-counter (OTC) products and other forms of investment for over a decade. In October 2023, GrayScale filed with the SEC to convert one of its OTC products (GBTC) into an ETF on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE).
- Fidelity: Fidelity, with a diverse range of services from financial planning to investment management and brokerage, currently facilitates direct investments in crypto through Fidelity Crypto®. In addition to their existing services, Fidelity has sought approval for a Bitcoin ETF, introducing amendments focused on enhancing user safety and risk disclosures, with the most recent amendment filed in October 2023.
- VanEck: A leader in the ETF and mutual fund space, VanEck offers a variety of ETFs, from municipal bonds to those based on social sentiment. While they already have a Bitcoin Strategy ETF (XBTF) using futures, their proposed spot Bitcoin ETF is designed to cater to traditional asset managers, potentially allowing them to carve out a niche in a saturated market. The XBTF has achieved impressive year-to-date returns of over 100%.
- Franklin Templeton: Boasting over $1.5 trillion in Assets Under Management (AUM), Franklin Templeton is one of the largest investment firms globally. Specializing in a vast array of mutual funds, with over 450 options for clients, they have applied for a spot Bitcoin ETF. The SEC recently deferred the decision on Franklin Templeton’s spot Bitcoin ETF from November 2023 to early 2024.













