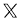$77293.473
At CoinCu News, we give both basic and in-depth articles on the latest news in the cryptocurrency and blockchain sectors.
Mayowa is a seasoned freelance writer specializing in creating compelling, high-converting content across diverse industries.
With extensive experience working with major news outlets, personal blogs, and private clients, he brings a deep understanding of audience engagement and storytelling. His expertise spans SEO optimization, persuasive copywriting, and niche versatility, ensuring content that resonates and delivers results.
Armed with a strong command of the English language and a keen eye for detail, he crafts content that is both impactful and strategically tailored to meet client goals.
News
China Raises Tariffs on U.S. Goods to 84%
China hikes U.S. import tariffs from 34% to 84% amid trade tensions.
Apr
Argentine President Under Investigation for LIBRA Cryptocurrency Scandal
President Javier Milei faces an inquiry into his involvement in the LIBRA cryptocurrency allegations. Learn
Apr
U.S. Senate Schedules Vote on SEC Chair Nominee Atkins
SEC nominee Paul Atkins faces a crucial Senate vote, potentially reshaping crypto regulations and market
Apr
Argentine House Probes Libra Memecoin Scandal Involving President
Argentine lawmakers investigate President Milei over $LIBRA memecoin, after a dramatic value crash, triggering significant
Apr
DOJ Revises Cryptocurrency Enforcement: Developers Safe from Liability
DOJ memo shields developers from liability, targets criminal misuse, impacting crypto markets.
Apr
Argentine Committee to Investigate LIBRA Cryptocurrency Scandal
The Argentine Congress forms a committee to investigate the LIBRA scandal involving President Milei and
Apr
Cboe BZX Files for Canary SUI ETF With SEC
Cboe BZX seeks SEC approval for the Canary SUI ETF, aiming to list and trade
Apr
Senate Schedules Vote on SEC Chairman Nominee Paul Atkins
U.S. Senate plans a vote on SEC nominee Paul Atkins, impacting cryptocurrency regulation.
Apr
US Initiates Higher Tariffs to Enhance Fair Trade
Upcoming changes in US trade policy will initiate higher tariffs affecting over 50 countries, aiming
Apr
[tptn_list how_old="7" limit="5" title_length="0" heading="0" show_date="0" ]
[tptn_list how_old="30" limit="5" title_length="0" heading="0" show_date="0" ]
Lastest
Global Leaders Gather at Strategic Bitcoin Reserve Summit 2025 Event
Online, United States
Bitcoin Summit