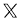$117468.728
At CoinCu News, we give both basic and in-depth articles on the latest news in the cryptocurrency and blockchain sectors.
Mayowa is a seasoned freelance writer specializing in creating compelling, high-converting content across diverse industries.
With extensive experience working with major news outlets, personal blogs, and private clients, he brings a deep understanding of audience engagement and storytelling. His expertise spans SEO optimization, persuasive copywriting, and niche versatility, ensuring content that resonates and delivers results.
Armed with a strong command of the English language and a keen eye for detail, he crafts content that is both impactful and strategically tailored to meet client goals.
News
SharpLink Purchases 10,000 ETH to Bolster Ethereum Staking
SharpLink Gaming acquires 10,000 ETH for $25.7M to support Ethereum staking, boosting market confidence.
Jul
U.S. Imposes 30% Tariff on EU Goods by August
Trump's 30% tariff on EU goods begins August 1, impacting $605 billion in imports.
Jul
Hafu Securities Gains Approval for Virtual Asset Trading in Hong Kong
Hafu Securities secures Hong Kong regulator's nod for virtual asset trading services.
Jul
PUMP Token Public Sale Concludes in Record Time
PUMP token raises $600M swiftly, gaining attention for pump.fun's impactful Solana venture.
Jul
U.S. House Begins ‘Crypto Week’: Key Legislation Proposed
The U.S. House's 'Crypto Week' advances major crypto legislation, impacting regulation and market strategy.
Jul
US House Commences ‘Crypto Week’, Key Bills Under Review
US House's 'Crypto Week' features key cryptocurrency regulations, impacting stablecoins and digital assets. Regulatory clarity
Jul
Upexi Raises $200 Million to Boost Solana Holdings
Upexi secures $200M financing to double Solana holdings, led by Big Brain Holdings.
Jul
Pump.fun Acquires Kolscan for Real-Time Trading Updates
Pump.fun acquires Kolscan, enhancing wallet tracking and trading analytics, focusing on top on-chain traders.
Jul
Inception Protocol Shuts Down Due to Market Challenges
Inception Protocol, built on EigenLayer, ceases operations citing product-market fit issues and lack of liquidity
Jul
[tptn_list how_old="7" limit="5" title_length="0" heading="0" show_date="0" ]
[tptn_list how_old="30" limit="5" title_length="0" heading="0" show_date="0" ]